The Most Commonly Used Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Major Drug Categories
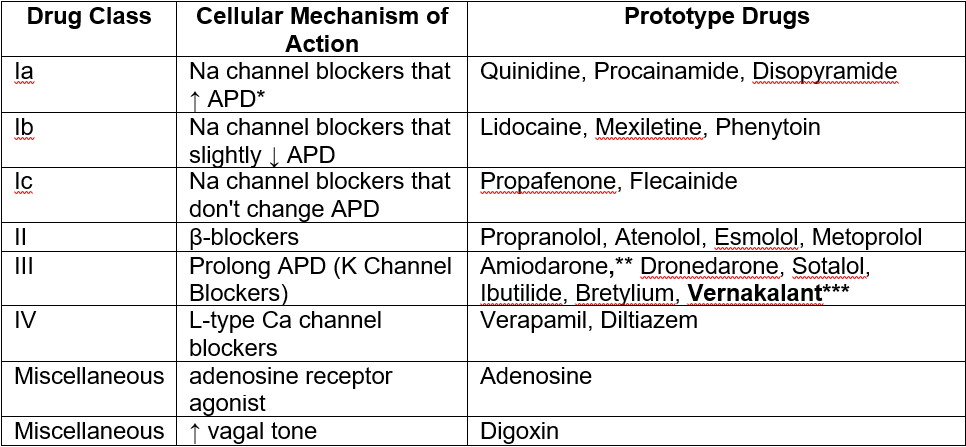
* APD– Action Potential Duration
** Amiodarone has Class I thru Class IV effects, but Class III effects seem to be most prominent.
*** Vernakalant is classified as class I as well.(1)
Mechanism of Action³
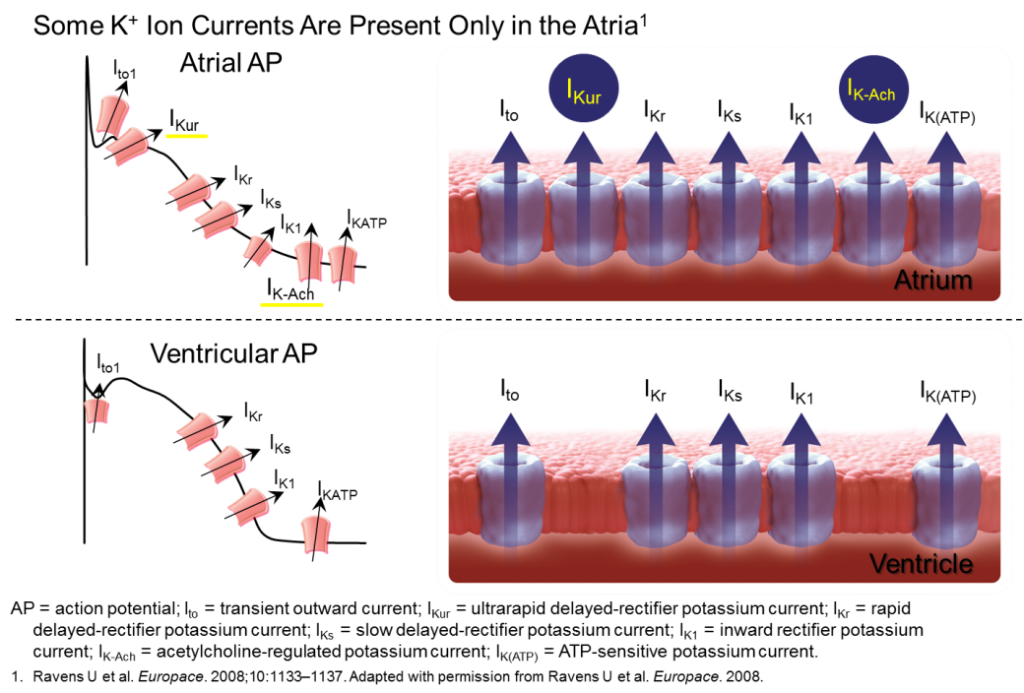
Vernakalant (Kynapid) is a newly discovered aminocyclohexyl ether (3-pyrrolidinol, 1-[(1R, 2R)-2-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethoxy] Cyclohexyl]-B hydrochloride (3R)-) that acts selectively on atrial tissue. Vernakalant is able to selectively affect the atrium because it targets 2 channels that are mainly found in the atria and not in the ventricles. The first is the Kv1.5 channel, which carries the ultra rapid delayed rectifier potassium current IK(ur). The second is the Kir3.1/3.4channel, which carries the acetylcholine dependent potassium current IK(Ach). Apart from its actions on the above channels, vernakalant can also work to block other ion currents as well, including Ito, late Ina, with minor blockade of IKr currents. The blockade of late Ina current is rate-dependent with fast offset kinetics, which means that blockage of the current is most significant at higher frequencies. This, in turn, can selectively slow conduction velocity in the atrium for those with atrial tachyarrhythmias, but not the ventricles. The blockade of the Ito current is through Kv4.3 channels, and is similar to late Ina, due to the fact that it too is rate-dependent and works to selectively prolong repolarization in the atrium for those patients with atrial tachyarrhythmias.
References:
-
עלון לרופא.
-
From: http://tmedweb.tulane.edu/pharmwiki/doku.php/intro_to_antiarrhythmics
- Vernakalant A New Drug to Treat Patients With Acute Onset Atrial Fibrillation. Page 41, 42.